Effective Gum Disease Treatment: Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions
Gum disease, if left untreated, can lead to severe consequences, including tooth loss and damage to the underlying bone. Fort Wayne dentist, Dr. David Painter, breaks down what gum disease is, its treatment options, and how to prevent the disease from developing.
Understanding Gum Disease
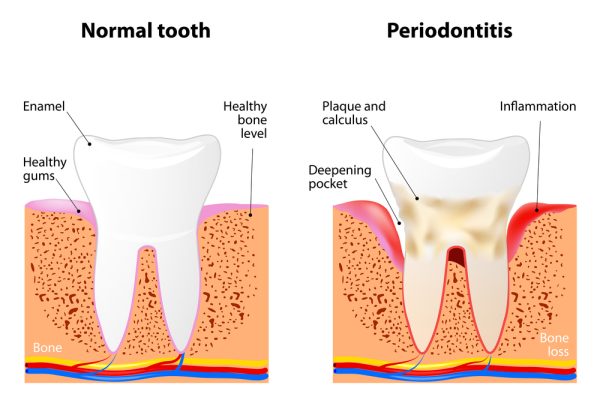
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque and tartar on teeth surfaces. This buildup leads to inflammation of the gums, characterized by redness, swelling, tenderness, and bleeding upon brushing or flossing.
Inflammation is a crucial marker of periodontal disease, and when left untreated, can progress from its initial stage called gingivitis to a more severe form called periodontitis. Periodontitis affects not only the gum tissue but also the bone and ligaments supporting the teeth, which may ultimately necessitate tooth removal.
Inflammation and Gum Disease
Inflammation is the body’s response to trauma or infection, often manifesting as redness, swelling, warmth, and pain. Gingivitis, the least severe form of periodontal disease, is typically caused by a bacterial infection resulting from an accumulation of plaque.
Fortunately, with diligent brushing, flossing, and routine professional dental care, symptoms of gingivitis can be reversed. However, when left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, an advanced form of periodontal disease that affects the bone and ligaments supporting the teeth which can result in tooth loss.
Types of Periodontal Disease
There are several types of periodontal disease, including gingivitis, periodontitis, aggressive periodontitis, and necrotizing periodontal diseases. Gingivitis, the initial stage of gum disease, can cause bleeding or swollen gums, halitosis, and bright red or purplish gums.
In more advanced stages, such as periodontitis, symptoms may include red, swollen, tender, or bleeding gums, loose or sensitive teeth, and potential bone loss. Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent the progression of gum disease and its detrimental effects on oral health.
Identifying Risk Factors
Several risk factors contribute to periodontal disease, including:
- Inadequate oral hygiene
- Smoking/tobacco use
- Heredity, stress, or certain medications
- Clenching or grinding of the teeth
- Systemic diseases
- Inadequate nutrition
- Age
By understanding these risk factors, you can take preventive measures to maintain healthy gums and avoid the onset of periodontal disease.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors such as poor oral hygiene, smoking, alcohol consumption, hormonal changes, poor nutrition, and obesity can potentially lead to an increased risk of gum disease. For example, tobacco use can significantly contribute to the deterioration of gum health.
Girls or women may experience an increase in the intensity of periodontal disease due to hormonal changes. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, practicing oral hygiene habits, and being aware of these factors can help minimize the risk of developing gum disease.
Health Conditions
Certain health conditions can exacerbate gum disease. Diabetes, for instance, can reduce your capacity to resist infection, thus intensifying gum disease. Additionally, family genetics can make some individuals more predisposed to developing severe periodontal disease.
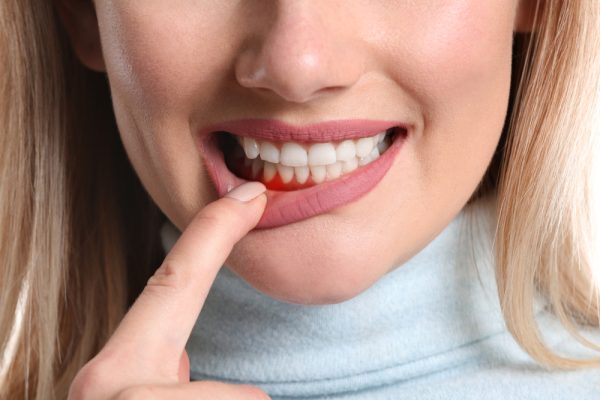
Recognizing Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of gum disease is crucial for early detection and treatment. Healthy gums are firm and pink, while signs of periodontal disease include redness, swelling, tenderness, bleeding, and receding gums.
By being vigilant and noticing any changes in the appearance or sensation of your gums, you can seek prompt dental care and prevent the progression of gum disease.
Early Signs
The initial indications of periodontal disease include swollen, tender, reddish, or purplish gums, gums that bleed when brushing or flossing, persistent bad breath or bad taste, and gums that are tender to the touch.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a dental health professional for an evaluation and proper treatment to prevent the progression of the disease.
Advanced Symptoms
Advanced symptoms of the disease may include red, swollen, tender, or bleeding gums, loose or sensitive teeth, bad breath, and potential bone loss. Receding gums, where the gum tissue is drawn away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth and root, is another indication of its progression.
If you experience any of these advanced symptoms, seek immediate dental care to prevent further damage and tooth loss.

Diagnosing Periodontal Disease
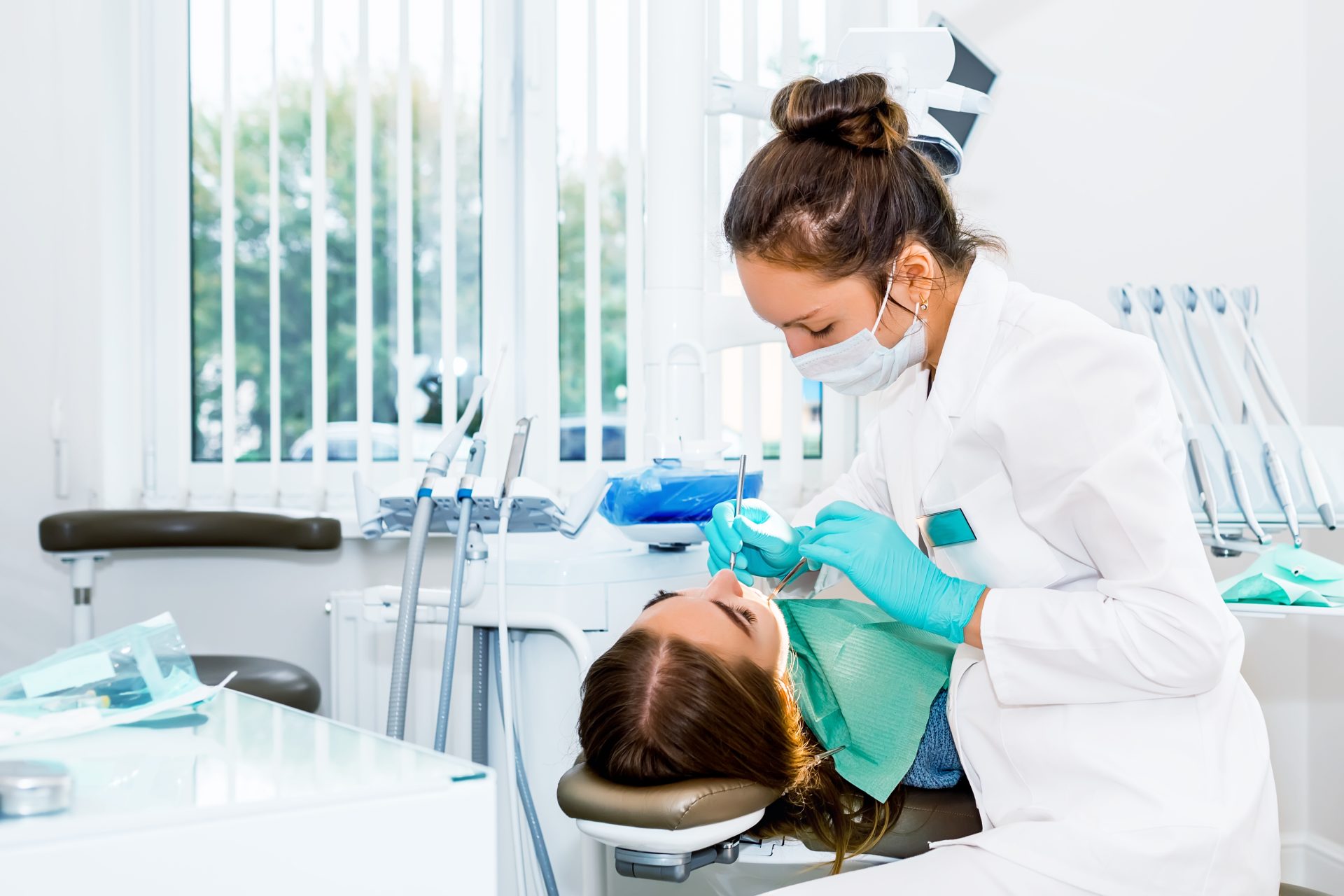
The diagnosis of periodontal disease can be done at your regular dental visits. It typically includes the following:
- Visual Examination: The dentist or dental hygienist will visually inspect your gums and gum tissue, looking for signs of inflammation, redness, swelling, and bleeding. They’ll also check for the presence of hardened plaque and tartar buildup on the teeth, which is one of the top warning signs of the disease.
- Probing: Using a dental instrument called a probe, the dental professional will measure the depth of the spaces (periodontal pockets) between your gums and teeth. Deeper gum pockets can be a sign of periodontal disease.
- X-rays: Dental X-rays may be taken to assess the bone supporting the teeth. X-rays can reveal bone loss, which is often associated with advanced gum disease.
- Gum Recession Assessment: The dentist will examine the gum line to determine if there are any recessions or loose teeth.
- Medical History and Symptoms: The dental professional will inquire about your medical history and any symptoms you may be experiencing, such as gum sensitivity, bad breath, or loose teeth.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
There are numerous non-surgical treatment options for gum disease available, such as keeping up with your oral hygiene at home, professional dental cleanings, and medications. These treatments can help manage gum disease in its early stages, and in some cases, even reverse its progression.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Excellent oral hygiene is the foundation of gum disease prevention and treatment. Regular teeth cleaning through brushing and flossing is essential for removing plaque and maintaining healthy gums.
It’s also vital to visit your dentist or dental hygienist regularly for checkups and cleanings to ensure your teeth and gums remain in optimal health.
Professional Dental Cleanings
Professional dental cleanings, such as scaling and root planing, are crucial for individuals with gum disease. This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar buildup from the teeth and gums, helping prevent symptoms of gum disease and its progression.
Regular dental cleanings can also help maintain healthy gums and prevent gum disease from developing in individuals with excellent oral hygiene.
Medications
Various medications can aid in gum disease treatment, including antibiotics, antimicrobial mouthwashes, and prescription-strength toothpaste. These medications can help control bacterial infections and reduce inflammation, supporting the healing process and preventing the progression of gum disease.
Your Fort Wayne dentist will recommend the most appropriate medication for your specific case.
Surgical Treatment Options
In some cases, non-surgical treatments may not be sufficient enough to manage gum disease, and surgical interventions may be necessary. Periodontal surgery and tooth extraction are two possible options for advanced gum disease treatment.
Periodontal Surgery
Periodontal surgery, such as pocket reduction surgery, gum grafts, or bone grafting, may be required for severe cases of gum disease that have caused gum or bone tissue loss. These procedures can help restore the health of your gums and teeth, prevent further damage, and improve the appearance of your smile.
Tooth Removal
Tooth removal may be suggested by a periodontist as a last resort to stop the infection caused by advanced gum disease. However, it’s not a guaranteed solution and dental surgery carries potential risks, such as discomfort, infection, and damage to adjacent teeth and gums.
It’s crucial to weigh the benefits and risks of tooth removal with your dental professional before making a decision.

Post-Treatment Care and Maintenance
Proper post-treatment care and maintenance are essential to ensure your gums heal properly and help prevent the recurrence of gum disease. This includes following your dentist’s instructions for post-treatment care, such as taking medications, abstaining from certain foods, and maintaining oral hygiene practices at home.
Recovery Time
Recovery time after gum disease treatment varies depending on the procedure. Scaling and root planing typically require no downtime, while more advanced techniques may need one to four weeks for complete recovery.
Ongoing Oral Care
Ongoing oral care is vital in preventing the recurrence of gum disease. This includes daily brushing and flossing, routine dental exams and professional cleanings, and maintaining oral hygiene at home.
Additionally, topical or oral antibiotics can be used to help control bacterial infection and support the healing process. By prioritizing your oral health, you can minimize the risk of gum disease and maintain a healthy, beautiful smile.
Choosing a Dental Professional
Selecting the right dental professional to treat gum disease is crucial for a successful outcome. While general dentists can treat mild cases of gum disease, severe cases typically require referral to a periodontist, a specialist in the treatment of gum disease.
Finding a specialist should involve thorough research and recommendations from trusted sources.
General Dentists vs. Periodontists
General dentists focus on providing comprehensive dental care, while periodontists specialize in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of gum disease.
If you have mild gum disease, your general dentist may be able to treat it effectively. However, in cases of severe gum disease, such as advanced periodontitis, your dentist may refer you to a periodontist for specialized care.
Finding a Specialist
To find a specialist for gum disease treatment, consider asking your general dentist for a referral or seeking recommendations from friends, family, or online reviews. Additionally, research the specialist’s education, experience, and professional affiliations to ensure they are well-qualified to treat your specific case. By choosing the right dental professional, you can ensure the best possible outcome for your gum disease treatment.

Frequently Asked Questions
Unfortunately, there’s no definitive way to cure gum disease, but with proper dental care and oral hygiene practices, it’s possible to effectively manage its progression and symptoms.
The quickest way to get rid of gum disease is by brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing regularly, using a fluoride mouth rinse, avoiding sugary foods and beverages, quitting smoking, and visiting your dentist at least twice a year.
Regular dental visits are essential to prevent gum disease and other oral health issues. Your dentist can detect early signs of gum disease and provide treatment to help you maintain healthy teeth and gums.
The best treatment for gum disease is a combination of professional cleaning from your dentist or periodontist, good oral hygiene at home, and antibiotics as needed. Professional cleaning removes plaque and tartar that can cause inflammation and gum disease, while good oral hygiene helps keep bacteria under control.
Antibiotics can help eliminate bacteria and reduce the damage caused by gum disease.
It’s never too late to treat gum disease. However, putting off treatment for periodontal disease can result in more invasive procedures to reverse the symptoms and get your dental health back on track. If the disease advanced into periodontitis, you may require surgeries such as bone grafts, pocket reduction surgery, or guided tissue regeneration.
Don’t Let Gum Disease Affect Your Health
Gum disease is a prevalent issue that affects a significant portion of the adult population. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to maintain your oral health and prevent the progression of this potentially damaging condition.
Remember, a healthy mouth is the foundation of a beautiful smile. Keep up with your dental hygiene and routine dental visits to ensure the best chances to prevent gum disease. And, if you suspect you may have gum disease, don’t hesitate to consult with our Fort Wayne dentist. Call our dental office at (260) 232-0280.
